The best way to predict the future is to create it, goes the saying. While the statement makes logical sense, it lacks the logistics between predicting the future and creating it. To create the future, we have to plan the steps that lead up to the predicted future. In the context of Demand Forecasting, it is about planning and executing all the steps which will help materialize the forecasted Demand.
Let’s begin understanding this deeper by analyzing why we need to forecast demand:
- There is a significant lead time between planning and execution of plans to run businesses at scale. Unlike restaurants (Which do not run at scale), where customers come and order food to be made on-demand, businesses require considerable execution time between point of creation of a product and point of consumption of a product.
- When a customer needs a product at the point of consumption, that consumption needs to be forecasted way in advance to be able to create the product and bring it to the customer on-time for consumption.
- Forecasting the demand allows businesses to derive the components that need to be executed to meet the forecasted demand.
- Demand Forecasting is also about setting Financial goals as an organization and acting on the required steps to achieve those goals.
Demand can be forecasted by taking many inputs into consideration:
- Company’s desired and targeted revenue goals
- Past demand and growth rate
- Marketing department’s plan and budget for demand generation
- Sales organization’s inputs on already committed customer orders and sales pipeline
- Current Production capacity and future capacity plans
- Available employee headcount and projected headcount
- Broader macroeconomic consideration
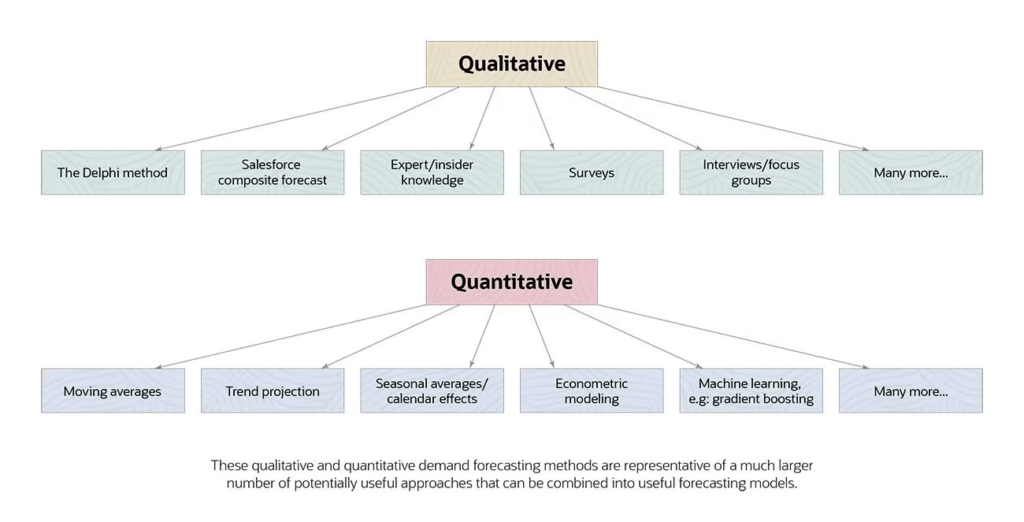
The Demand Forecasting Methods
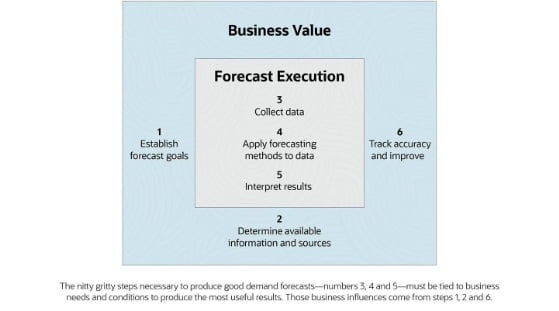
Demand can go through various rounds of revision before baselining. Once baselined, the demand for future periods need to be further revised on an ongoing basis, based on actual demand and many other dynamic factors as they materialize. Let’s understand how the forecasted demand results in planning for all underlying execution steps:
Sales and Marketing Plan
The Demand Forecast, amongst many other things, can be greatly related to ambitious target goals for the business. The forecasts may defy past demands and growth trends for both the company as well as the industry. Such aggressive forecasts call for proportionate support with equally aggressive plans for the Sales and Marketing functions. The marketing channels, budget for each channel and number of personnel in Marketing will need to be determined to generate the volume of Sales opportunities required to drive the forecasted demand. Similarly, the Sales organization needs to derive the count of sales folks necessary in various territories to handle the forecasted volume of sales opportunities for achievement of the forecasted demand.
Production Plan
For the organization to achieve the forecasted demand, it needs to fulfill the estimated sales orders that will contribute towards the forecast. Each of those projected sales orders will derive the quantities of different products that need to be delivered to the customers to recognize the targeted revenue. Depending on the organization, these products could be few or many. For each of these products, the estimated sales quantity needs to be produced and shipped to customers. The following high level steps will make it possible to come up with a Production plan:
- For each product, how many quantities need to be produced in each period (Day/week/month)
- For each product, how long does it take to produce
- How much quantity can be produced in each manufacturing work order or batch
- How many manufacturing work orders need to be performed for each product
- When should each of those manufacturing work orders start and finish
- Which center should these work orders be executed from
- What are the different steps in each work order and what is the schedule to be adhered to
- What machine units in the production center will be used to execute the different steps
- Who should execute each of the steps in each work order
Procurement Plan
We analyzed in the above section, how we can translate the demand forecast to derive the production plan. Similarly, we need to work out the purchase plan to be able to support the production plan. We need to follow the below steps to be able to generate a Procurement Plan:
- Review the quantities of different products that need to be produced in each period
- Analyze the recipes available to produce the products
- Identify the quantity of different raw materials required using each recipe to manufacture one unit of the product
- Derive the total quantities required of each raw material and at what time to be able to meet the Production plan schedule
- Determine the supplier of the raw material based on the production center and look up the lead time
- Generate planned purchase orders with raw material, quantity and required delivery date
Production Capacity Plan
We reviewed in the above sections how we derive the Production plan and Procurement plan to be able to generate the forecasted demand. Now, to produce the required finished goods quantity, every organization requires factory capacity in addition to raw materials to be purchased. The factory capacity required to support the production plan can be generated by looking at:
- How much quantity of finished goods need to be produced
- How long it takes each machine unit to completely execute a work order
- How much maximum quantity a machine unit can produce in one work order
- How many machine units are required to produce the required finished products
- How many factories can accommodate the required machine units
In most cases, the plan can generally be met with the existing production capacity in an organization, in the short run. However, in some cases the existing capacity will not be sufficient to meet the predicted demand.
- In the long run, the demand will typically increase significantly more than the current demand. So manufacturing capacity needs to be incremented accordingly to be able to meet the production demand
- This will require Capital budgeting to add the capacity
- In some cases, organizations have aggressive growth targets. To be able to support the aggressive growth plan, manufacturing capacity needs to be augmented in a shorter time frame.
- This can be achieved by purchasing contract manufacturing capacity from third party manufacturers (CMOs)
Testing Plan
We know that everything produced in an organization needs to be tested and ensured that it meets the required quality standards. This is to assure acceptance of the products by customers and also to maintain the reputation of the company. In the case of Food and Drug production companies, the testing needs are all the more vigorous due to the critical impact they can have on human lives. That’s why Food and Drug production companies are regulated via very stringent quality testing requirements by national authorities to ensure public safety. So, for a company to be able to meet its demand forecast, it also needs to derive the testing plan supporting its production plan for customer shipments. The company needs to:
- Generate testing schedule for each work order
- Assign personnel to validate each production batch
Filling and Packing Plan
We all are customers in one way or another. We all receive products in well-packaged forms. That is a basic customer expectation. So for an organization to meet the demand forecast, just producing the required quantities of finished products is not enough. The finished product needs to be filled into different containers, packaged and labeled appropriately. So the production plan needs to be supported with:
- Filling schedule for each of the bulk-produced finished products from each manufacturing batch
- Packing schedule for each of the filled units
- Labeling of packaged units
- Testing of the labeled units before shipment
Distribution Plan
After the finished product is packed and labeled into units, they need to be transported to the customer locations. For the forecasted demand, there needs to be a transportation and distribution plan to ensure that the products reach the correct location during each period. This requires:
- Identifying the factory from where products need to be shipped to each distribution center
- Determining the model of transportation and the carrying capacity of each mode
- Derive the number of shipping containers required for each period between factory and distribution center
- Send the transportation orders to shipment carriers
Hiring Plan
In addition to all of the above resources, one of the key ingredients for achieving the plans of an organization is human resource. Every organization needs to generate the required personnel to be able to execute the plan required to meet demand forecasts. It is imperative to look at:
- How many staff are required to support the production plan
- How many personnel are needed to execute the Procurement plan
- How many human resources are required across all support functions to meet the demand forecast
- How many internal and external recruiters are required to address the human resource gap
- Create job requisitions and assign to recruiters to execute the hiring plan
Financial Plan
All of the above plans can not be executed unless the organization has the necessary financial resources. All the plans need to be amply supported with required financial capital. For this, Finance team needs to project:
- Cash required to support Procurement Plan
- Funding required to address Capacity requirements
- Budget required to hire the human resources
- Expenses to be incurred in executing the production plan
- Cost to be incurred in testing, packing, and distribution of products
- Determine the internal or external source of funds
- Plan to raise capital externally when required
In conclusion, we realize that while Demand Forecasting is a great starting point for an organization, there are several complex components that get generated based on the forecasted demand. In the absence of visibility into the status of all the required steps to meet growth targets, it is practically impossible to measure the health of the execution process. And the fact that demand forecasting and the underlying steps are dynamic on a daily basis, it is all the more important to have dynamic visibility available to stakeholders at different levels all the time. Analytics is the platform that can provide organizations with the ability to track progress and take corrective action as soon as required.