Introduction
This blog is the second one in a two-part series. In the first blog we had explored the role of data analytics technology in driving supply chain visibility in the ‘supply chain planning’ segment. In this blog, we’ll focus on how data analytics technology drives supply chain visibility across the ‘supply chain execution’ segment.
Role of Data Analytics in Driving Visibility in Supply Chain Execution
Supply chain execution segment focuses on the following areas of supply chain:

In the subsequent part of this blog, we will describe the role that data analytics can play in driving visibility in each of these areas.
1. Order Management
Order management/fulfillment involves receiving, processing, and fulfilling customer orders. This includes order entry, order confirmation, picking and packing, shipping, and delivery. The goal is to provide customers with accurate and timely order fulfillment while maintaining customer satisfaction.
Order management in pharmaceutical and life sciences companies suffers from siloed order systems across regions and channels, lack of real-time inventory visibility, manual tracking of order fulfilment, and limited integration between ERP, customer relationship management, and logistics platforms. These issues lead to delays, errors, and inefficiencies in meeting customer demand.
Data analytics can bridge these gaps by:
- Descriptive Analytics: Providing insights about historical order processing times, fulfilment rates, and customer satisfaction levels to understand current order management performance and identify areas for improvement
- Diagnostic Analytics: Providing insights about the causes of order delays, fulfillment errors, or customer complaints to identify inefficiencies and enhance order fulfillment effectiveness
- Predictive Analytics: Providing forecasts of future order volumes, potential fulfillment bottlenecks, and resource constraints to enable proactive order planning, streamline workflows, and reduce processing delays
- Prescriptive Analytics: Providing recommendations about optimal order processing workflows, order fulfillment strategies, and resource allocation to achieve the right balance between operational efficiency and customer satisfaction while improving overall order management responsiveness
2. Procurement
Procurement is the process of acquiring goods and services from external suppliers. This includes sourcing, negotiating contracts, issuing purchase orders, and managing supplier relationships. The goal is to obtain the best value for money while meeting quality, delivery, and regulatory requirements.
Procurement in pharmaceutical and life sciences companies is hindered by fragmented supplier data, lack of real-time spend visibility, limited risk assessment capabilities, and manual vendor performance tracking. These can lead to suboptimal sourcing decisions, supplier disruptions, and inflated costs, especially in a globally distributed and compliance-heavy environment.
Data analytics can remove this hindrance by:
- Descriptive Analytics: Providing insights about historical purchasing data, supplier performance, and contract terms to understand current procurement activities and identify areas for improvement
- Diagnostic Analytics: Providing insights about the causes of procurement delays, cost overruns, or quality issues to identify inefficiencies and enhance procurement effectiveness
- Predictive Analytics: Providing forecasts of future material prices, supplier performance trends, and potential supply chain disruptions to enable proactive procurement planning and reduce cost or supply risks
- Prescriptive Analytics: Providing recommendations about optimal sourcing strategies, supplier selection, and contract terms to achieve the right balance between cost efficiency, supplier reliability, and risk mitigation while strengthening overall procurement performance
3. Warehouse Management
Warehouse management involves the efficient storage and handling of goods within a warehouse or distribution center. This includes receiving, put-away, storage, picking, packing, and shipping. The goal is to optimize warehouse space, minimize handling costs, and ensure the accurate and timely fulfillment of orders.
Warehouse management in pharmaceutical and life sciences companies faces limited real-time visibility into inventory levels and locations, inadequate environmental monitoring (e.g., temperature, humidity), poor integration with upstream and downstream systems, and manual, error-prone tracking of controlled substances and serialized items. These issues can result in compliance risks, product spoilage, and inefficient space utilization.
Data analytics can plug these gaps by:
- Descriptive Analytics: Providing insights about historical warehouse operations data, including receiving, put-away, picking, packing, and shipping, to understand current warehouse performance and identify areas for improvement
- Diagnostic Analytics: Providing insights about the causes of warehouse bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or operational errors to find process constraints and enhance operational effectiveness
- Predictive Analytics: Providing forecasts of future warehouse capacity needs, potential operational bottlenecks, and workflow constraints to enable proactive planning, optimize space utilization, and reduce delays
- Prescriptive Analytics: Providing recommendations about optimal warehouse layouts, picking strategies, and resource allocation to achieve the right balance between efficiency, cost reduction, and improved order fulfillment responsiveness
4. Transportation Management
Transportation management involves the planning, execution, and control of the movement of goods from one location to another. This includes selecting transportation modes (e.g., truck, air, sea), optimizing routes, negotiating rates, and managing transportation providers. The goal is to deliver goods safely, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
Transportation management in pharmaceutical and life sciences companies suffers from shortcomings such as lack of real-time shipment tracking, limited visibility into cold chain conditions, poor coordination across carriers and regions, and manual incident reporting. These shortcomings increase the risk of delays, product spoilage, and non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
Data analytics can address these shortcomings by:
- Descriptive Analytics: Providing insights about historical transportation costs, delivery times, and route performance to understand current transportation operations and identify areas for improvement
- Diagnostic Analytics: Providing insights about the causes of transportation delays, cost overruns, or delivery issues to find inefficiencies and enhance delivery effectiveness
- Predictive Analytics Providing forecasts of future transportation needs, potential disruptions, and route constraints to enable proactive planning, reduce delays, and improve overall transport reliability
- Prescriptive Analytics: Providing recommendations about optimal transportation modes, route planning, and carrier selection to achieve the right balance between cost efficiency, delivery speed, and resource utilization while strengthening overall logistics performance
5. Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials and components into finished pharmaceutical products. This involves a series of operations, including mixing, blending, granulation, tableting, encapsulation, filling, and packaging. Manufacturing must adhere to strict GMP regulations to ensure product quality, safety, and efficacy.
Manufacturing in pharmaceutical and life sciences companies faces disconnected production systems, limited real-time visibility into equipment performance and batch quality, poor integration of shop-floor data with enterprise systems, and reliance on manual, paper-based processes. These challenges lead to production delays, quality deviations, and inefficient resource utilization.
Data analytics can address these gaps by:
- Descriptive analytics: Providing insights about historical production data, including output, defects, and downtime, to understand current manufacturing performance and identify areas for improvement
- Diagnostic analytics: Providing insights about the causes of production delays, quality issues, or equipment failures to find inefficiencies and enhance manufacturing effectiveness
- Predictive analytics: Providing forecasts of future production output, potential equipment failures, and workflow constraints to enable proactive planning, optimize production schedules, and reduce downtime
- Prescriptive analytics: Providing recommendations about optimal production schedules, resource allocation, and equipment maintenance strategies to achieve the right balance between efficiency, cost reduction, and product quality while improving overall manufacturing performance
6. Quality Management
Quality management encompasses all activities related to ensuring that pharmaceutical products meet the required quality standards. This includes quality control, quality assurance, and continuous improvement. Quality management systems are implemented to ensure that all processes and activities are performed in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.
Quality management in pharmaceutical and life sciences companies suffers from siloed quality data across functions, reliance on manual documentation, delayed detection of deviations, and limited ability to perform root cause analysis. These issues hinder quality decision making, increase compliance risks, and slow down batch release processes.
Data analytics can plug these issues by:
- Descriptive analytics: Providing insights about historical quality data, including defect rates, customer complaints, and inspection results to understand current quality performance and identify areas for improvement
- Diagnostic analytics: Providing insights about the causes of quality defects, customer complaints, or process variations to find inefficiencies and enhance quality control effectiveness
- Predictive analytics: Providing forecasts of potential quality issues, future defect occurrences, and process variations to enable proactive quality management and reduce risks
- Prescriptive analytics: Providing recommendations about optimal quality control processes, inspection strategies, and corrective actions to achieve the right balance between product quality, defect reduction, and customer satisfaction while strengthening overall quality performance
7. Returns Management
Returns management involves the process of handling returned products. This includes receiving, inspecting, and processing returned goods. The goal is to minimize losses, comply with regulations, and protect the company’s reputation.
Returns management in pharmaceutical and life sciences companies faces challenges such as lack of real-time tracking of returned products, poor visibility into return reasons and conditions (e.g., expired, damaged, temperature-excursion), manual and inconsistent returns processing, and limited integration with inventory and quality systems. These gaps lead to revenue leakage, compliance risks, and inefficient product disposition.
Data analytics can address these challenges by:
- Descriptive analytics: Providing insights about historical returns data, including return rates, reasons for returns, and associated costs to understand current returns performance and identify areas for improvement
- Prescriptive analytics: Providing insights about the causes of product returns, such as defects, damage, or customer dissatisfaction to find inefficiencies and enhance returns management effectiveness
- Diagnostic analytics: Providing forecasts of future return rates, potential return issues, and process constraints to enable proactive returns planning and reduce operational and financial risks
- Predictive analytics: Providing recommendations about optimal returns processes, reverse logistics strategies, and product refurbishment or disposal options to achieve the right balance between cost efficiency, customer satisfaction, and value recovery while improving overall returns performance
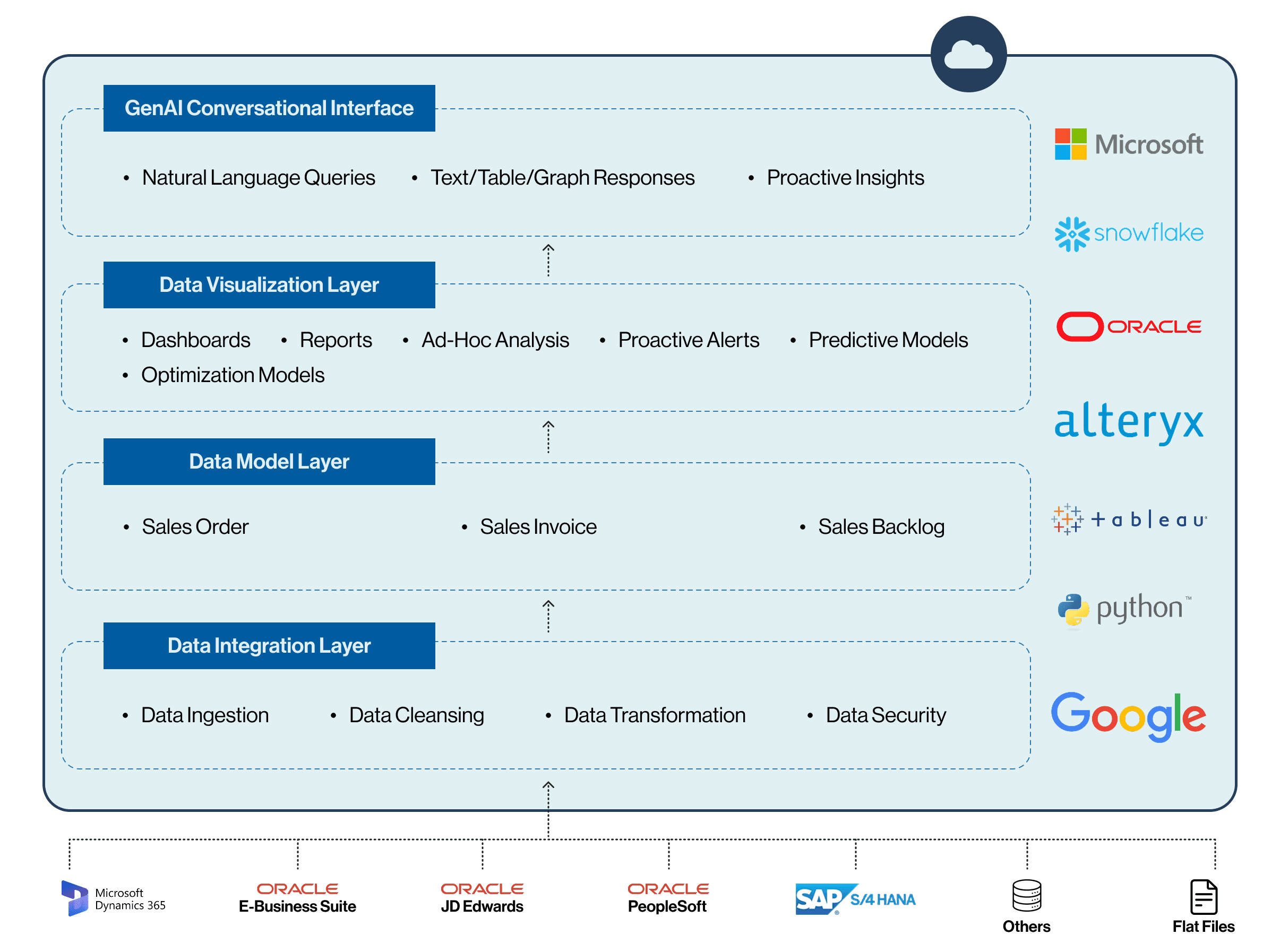
DiLytics Prebuilt Supply Chain Execution Insight Solution
DiLytics has built a supply chain execution solution, branded as DiLytics Supply Chain Execution Insight Solution, that provides the above-mentioned functionalities/capabilities for the pharmaceutical and life sciences industry. DiLytics Supply Chain Execution Analytics Solution comes prebuilt with:
- Industry–leading data model
- Data pipelines from leading ERPs
- A rich library of reports, dashboards, and metrics
- Conversational interface

A high-level architecture of DiLytics Supply Chain Planning Insight Solution is provided below:
Conclusion
In the world of pharmaceutical and life sciences supply chains, execution excellence is paramount. From procurement and manufacturing to warehousing, transportation, and returns management, data analytics turns supply chain execution from a black box to a glass box – transparent, intelligent and responsive. By leveraging descriptive to prescriptive analytics, companies can ensure product quality, regulatory compliance, and on-time delivery while reducing operational risks and inefficiencies. Data analytics, therefore, has the power to transform supply chain execution from just a function to a true competitive differentiator for pharmaceutical and life sciences companies.